Microsoft has released critical security updates for Exchange Server, marking a significant milestone as these represent the final publicly available updates for Exchange Server 2016 and 2019. The October 2025 Security Updates (SUs) address multiple vulnerabilities across Exchange Server Subscription Edition (SE), Exchange Server 2019, and Exchange Server 2016.
Affected Versions and Availability
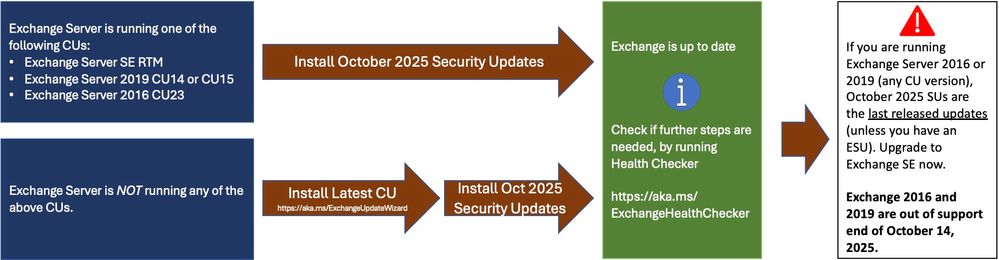
The October 2025 security updates are available for the following Exchange Server versions:
- Exchange Server Subscription Edition (SE) RTM
- Exchange Server 2019 Cumulative Update 15 (CU15)
- Exchange Server 2019 Cumulative Update 14 (CU14)
- Exchange Server 2016 Cumulative Update 23 (CU23)
Exchange Online customers are already protected from these vulnerabilities and do not need to take action beyond updating any on-premises Exchange servers or Exchange Management Tools workstations in their environment.
Critical Vulnerabilities Addressed
Microsoft has patched three important vulnerabilities in this security update, all classified as elevation of privilege or spoofing attacks:
CVE-2025-53782: Microsoft Exchange Server Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability with a CVSS score of 7.3. This vulnerability involves an incorrect implementation of authentication algorithm that allows an unauthorized attacker to elevate privileges locally.
CVE-2025-59248: Microsoft Exchange Server Spoofing Vulnerability with a CVSS score of 7.5. This flaw involves improper input validation that allows an unauthorized attacker to perform spoofing over a network.
CVE-2025-59249: Microsoft Exchange Server Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability with a CVSS score of 7.7. This represents the highest severity vulnerability in the October update.
Although Microsoft is not currently aware of any active exploits in the wild, the company strongly recommends immediate installation of these updates to protect Exchange environments from potential security risks.
End of Support for Exchange 2016 and 2019
The October 2025 security updates represent a critical turning point for organizations running Exchange Server 2016 and 2019. These versions have officially reached end of support as of October 14, 2025. This means Microsoft will no longer provide security updates, time zone updates, technical support, or bug fixes for these versions through public channels.
Organizations that have not upgraded will face significant security risks by continuing to operate unsupported Exchange servers. However, Microsoft has offered a limited Extended Security Update (ESU) program for customers who need additional time to migrate.
Extended Security Update Program Details
The ESU program provides a six-month extension for organizations that contacted their Microsoft Account Teams, offering security updates only through April 2026. However, Microsoft strongly recommends upgrading to Exchange Server Subscription Edition rather than relying on the ESU program as a long-term solution.
An important consideration for ESU customers is that starting with Exchange SE Cumulative Update 2 (CU2), coexistence with Exchange 2016 and 2019 will no longer be supported, as CU2 will block installation if any build of Exchange 2016 or 2019 is present in the organization.
Auth Certificate Export Restrictions
Starting with the October 2025 security update, Microsoft has implemented an important security enhancement regarding the Exchange Server Auth Certificate. Exporting the Auth Certificate and its private key using the Export-ExchangeCertificate cmdlet is now blocked for added security, as detailed in KB5069337.
The Auth Certificate is crucial for securing Exchange Server workloads, and exporting its private key is rarely needed in legitimate scenarios. For troubleshooting Auth Certificate issues, Microsoft recommends using the MonitorExchangeAuthCertificate PowerShell script instead of attempting to export the certificate.
Update installation
The following update paths are available:
- Inventory your Exchange Servers to determine which updates are needed using the Exchange Server Health Checker script. Running this script will tell you if any of your Exchange Servers are behind on updates (CUs, SUs, or manual actions).
- Install the latest CU. Use the Exchange Update Wizard to choose your current CU and your target CU to get directions.
- Re-run the Health Checker after you install an update to see if any further actions are needed.
- If you encounter errors during or after installation of Exchange Server, run the SetupAssist script. If something does not work properly after updates, see Repair failed installations of Exchange Cumulative and Security updates. Also please see File version error when you try to install Exchange Server updates.
FAQs
Hybrid Environment Update Requirements
Organizations running Exchange in hybrid mode with Exchange Online must install the October 2025 security update on their on-premises Exchange servers, even if those servers are used exclusively for management purposes. While Exchange Online is already protected against these vulnerabilities, the on-premises infrastructure requires patching to maintain security and compatibility. An important consideration is that if you modify the Auth Certificate after installing the security update, you must re-run the Hybrid Configuration Wizard to ensure continued proper operation of the hybrid environment.
Cumulative Update Installation Process
The security updates are cumulative, which significantly simplifies the patch management process. If your Exchange servers are running a Cumulative Update (CU) that is supported by the latest security update, you do not need to install all intermediate security updates (SUs) or hybrid updates (HUs) in sequential order. You can skip directly to installing the latest security update, saving considerable time and reducing deployment complexity. This cumulative nature means organizations that may be several months behind on security patches can catch up with a single installation rather than applying multiple updates sequentially. Please see this blog post for more information.
Comprehensive Deployment Scope
Microsoft strongly recommends installing security updates on all Exchange Servers within the organization, including both production servers and those running only the Exchange Management Tools role. This comprehensive approach ensures compatibility between management tools clients and servers, preventing potential version mismatch issues that could disrupt administrative functions. The recommendation extends to all servers and workstations that have the Exchange Management Tools installed, not just the Exchange servers themselves. For specialized scenarios where you need to update Exchange Management Tools in an environment with no running Exchange servers, Microsoft provides guidance through their documentation to handle this edge case properly.
Fortify Your Server with Messageware Security
Data breaches have increased by 72%, servers are compromised in under 90 minutes. Ensure you have multiple layers of security software protecting your Windows Servers.
Z-Day Guard for All Windows Servers: Next-gen server protection, providing detection, alerting, and response (MDR) to zero-day and server penetration cyber-attacks. Leverages embedded monitoring technology that cannot be turned off by malicious software. No need to research complicated deployments and no learning curve to install and manage.
EPG Guard for Exchange Servers: Real-time security. Stop AD account lockouts, eliminate password attacks, intelligent GEO blocking, and prevent Exchange Server vulnerability probing.
Don’t leave your critical infrastructure vulnerable, be proactive and stay ahead of evolving threats.